 Multi-section clamping diaphragm coupling1. Diaphragm elastic coupling 2. Gaoling...
Multi-section clamping diaphragm coupling1. Diaphragm elastic coupling 2. Gaoling... HL type elastic pin couplingThe elastic pin coupling (GB5014-85) is suitable for...
HL type elastic pin couplingThe elastic pin coupling (GB5014-85) is suitable for...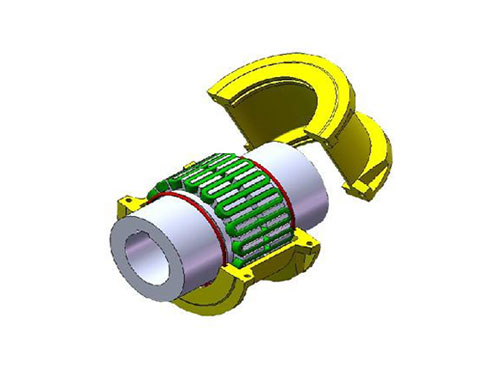 JS type housing radial mounting type couplingSelection of JS type housing radial mounting type coupling...
JS type housing radial mounting type couplingSelection of JS type housing radial mounting type coupling... TB type HG5-251-69 standard rackThe standard frame of TB type HG5-251-69 is "glass-lined...
TB type HG5-251-69 standard rackThe standard frame of TB type HG5-251-69 is "glass-lined... Elastic sleeve pin coupling for pumpElastic sleeve pin coupling for pump: 1. Elastic...
Elastic sleeve pin coupling for pumpElastic sleeve pin coupling for pump: 1. Elastic...The failure principle of coupling misalignment and the choice of taper sleeve type elastic diaphragm coupling
XNUMX. The failure principle of the misalignment of the coupling
1. Misalignment fault characteristics
Vibration frequency characteristics: The vibration frequency of angular misalignment is the main frequency vibration, f=2πΩ, and the axial vibration is greater than the radial vibration.Parallel misalignment is dominated by radial vibration with 2X axial frequency, and 2X in the frequency spectrum often exceeds the doubling frequency.When the parallelism and angular misalignment are serious, there will be a lot of high-order harmonic vibration.
Vibration phase characteristics: when there is an angular misalignment, the radial vibration is in phase, while the axial vibration has a phase difference of 180°; the phase characteristics of parallel misalignment are: the phase difference between the two sides of the coupling is 180°, and the radial vibration is large and incorrect. The stronger the medium, the closer the phase difference is to 180°.
The dynamic characteristics of speed tracking: the vibration changes with the change of speed, load and oil temperature, but the influence of pressure and flow change on the vibration is not obvious.
Axis orbit: When the misalignment is not obvious, the axis orbit is elliptical; when the misalignment reaches a moderate degree, the axis is banana-shaped; when it is severe, it has an outer "8" shape.
2. Definition of misalignment
The rotors of the unit are connected by couplings to transmit movement and torque. When the unit is running, the axes of the rotors are not parallel or coincident, which results in the inclination or eccentricity of one or several bearing assembly, which is called misalignment. .It is divided into two categories: coupling (shafting) misalignment and bearing misalignment.Usually misalignment refers to misalignment of the coupling (shafting).Coupling misalignment is divided into three types: parallel misalignment, angular misalignment and comprehensive misalignment.
3. Reasons for misalignment
(1) Errors or insufficient adjustments during installation of the machine;
(2) The distortion of the flexible support caused by the torque;
(3) Deformation of the machine caused by stable changes;
(4) The rigidity of the foundation is insufficient or the settlement of the foundation is not uniform, etc.
4. Misalignment vibration mechanism
Large-scale rotating machinery often uses gear couplings, which are composed of an intermediate gear sleeve with an external gear ring and an internal gear ring.When the alignment is good, only the circumferential force that transmits the torque is generated between the inner and outer gear sleeves; when there is a misalignment, the contact points of the inner and outer gear surfaces change, resulting in a relative tilt of the intermediate gear sleeve, which causes additional radial force when transmitting motion and torque And axial force, vibration is generated.With the development of technology, the various performance advantages of diaphragm couplings have been highlighted, and they are gradually replacing the application of drum-shaped gear couplings in various large-scale machines.
Second, the classification of ventilators
Ventilators are generally divided into three categories according to their purposes: main fan fans are used for the ventilation of the entire mine or a certain wing of the mine; auxiliary fans are used to adjust the air volume of the mine ventilation branch; local fans are used for the inside of the mine. There is no through-wind or local ventilation in unopened tunnels.According to the flow direction of the airflow after entering the impeller, the fans can be divided into three types: axial fans, centrifugal fans and diagonal (mixed flow) fans.
Nowadays, the underground ventilation equipment in coal mines is mostly a counter-rotating axial fan.It adopts a guide vane shape, and the main components include casing, blades, guide vane ring, motor rotor, bearing system, intermediate shaft, coupling, housing, diffuser, etc.The axial flow fan has the following characteristics: relatively compact structure, small size, relatively light weight (about 60%-70% of the same unit as the centrifugal fan), can be directly driven at high speed, and the transmission method is relatively simple.
XNUMX. Vibration failure of the fan
Fans are key equipment in industrial and mining applications. Their quality directly affects the normal operation of coal mines. Fan failures are mostly reflected in the vibration state, especially large and medium-sized fans. The vibration is not only strong and complex, and it is quite complicated to handle. Time-consuming.Generally, among all vibration failure factors, 8 types of failures are common: mass imbalance, rotor friction, misalignment, bearing damage, shaft cracks, bearing looseness, coupling damage, and clearance.
Points for attention when choosing the correct choice of tapered sleeve type elastic diaphragm coupling:
XNUMX. Taper sleeve type elastic diaphragm coupling is often used in servo systems. The diaphragm has good torque rigidity, but it is slightly inferior to the bellows coupling.
XNUMX. On the other hand, the taper sleeve type elastic diaphragm coupling is particularly delicate, and it is easy to be damaged if it is misused or not installed correctly during use.Therefore, it is especially important to determine that the deviation is within the tolerance range of the normal operation of the coupling.
XNUMX. Adjust the model according to the shaft diameter:
The initially selected coupling dimensions of the bearing coupling, that is, the shaft hole diameter d and the shaft hole length L, should meet the requirements of the shaft diameters of the driving and driven ends, otherwise the coupling specifications must be adjusted according to the shaft diameter d.
It is a common phenomenon that the shaft diameters of the main and driven ends are different. When the torque and speed are the same, and the shaft diameters of the main and driven ends are different, the coupling model should be selected according to the larger shaft diameter.In the newly designed transmission system, the seven shaft hole types specified in GBT3852 should be selected, and the J1 shaft hole type is recommended to improve versatility and interchangeability. The shaft hole length is in accordance with the provisions of the i-bearing coupling product standard .
XNUMX. Taper sleeve type elastic diaphragm coupling consists of at least one diaphragm and two shaft sleeves.The diaphragm is fastened to the shaft sleeve with a pin and generally does not loosen or cause backlash between the diaphragm and the shaft sleeve.Some manufacturers provide two diaphragms, and some provide three diaphragms, with one or two rigid elements in the middle, and the two sides are connected to the shaft sleeve.
1.5. Taper sleeve type elastic diaphragm couplings are a bit like bellows couplings. In fact, couplings transmit torque in the same way.The diaphragm itself is very thin, so it is easy to bend when the relative displacement load is generated, so it can withstand up to XNUMX degrees of deviation, while generating a lower bearing load in the servo system.